Introduction
On January 21, 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump reignited a controversial proposal—the acquisition of Greenland by the United States. Highlighting its strategic importance for “international security,” Trump’s remarks underscore a broader geopolitical chess game in the Arctic. Greenland’s vast natural resources, strategic location, and critical role in Arctic security have made it a focus of global power dynamics. This article explores why Greenland is indispensable in the realm of national security, military readiness, and resource control.
Greenland’s Geostrategic Value
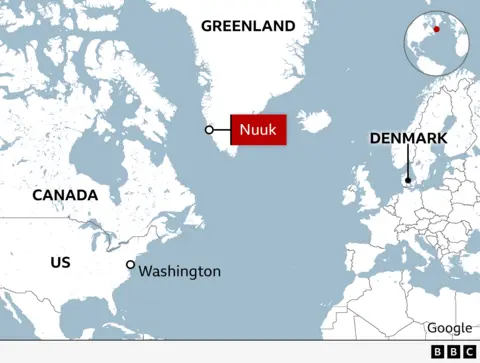
Proximity to Russia and China Greenland’s geographic position is a linchpin for strategic defense systems. Nestled between North America and Europe, the island enables enhanced monitoring of adversarial activities in the Arctic. Russia’s aggressive expansion, including reopening Soviet-era bases and deploying advanced hypersonic missile systems, has amplified tensions in the region. Simultaneously, China’s Polar Silk Road initiative signifies Beijing’s ambitions to integrate Arctic trade routes and resources into its global strategy. For the U.S., maintaining situational awareness and leveraging Greenland’s location is crucial for preemptive threat detection.
Arctic Militarization The Arctic’s escalating militarization highlights the strategic urgency of Greenland. Thule Air Base, operated by the U.S. Space Force, is critical for ballistic missile early warning systems, space domain awareness, and satellite communications. As Arctic rivals like Russia fortify their Northern Fleet and China increases its dual-use infrastructure in the region, Greenland’s operational importance for NATO and the U.S. Department of Defense continues to grow. Ensuring force readiness and maintaining a robust command-and-control structure in Greenland is imperative for regional stability.
The Economic Dimensions of Greenland
Greenland’s Natural Resources Greenland’s reserves of rare earth elements (REEs), essential for military hardware, renewable energy technology, and advanced electronics, represent a critical supply chain asset. With global reliance on China for REEs, securing Greenland’s resources would mitigate vulnerabilities in U.S. defense logistics. Additionally, Greenland’s untapped oil and gas reserves provide strategic energy diversification opportunities, reducing dependency on hostile or unstable regions.
Trade Routes and Melting Ice Climate change is transforming Greenland’s strategic calculus. Melting Arctic ice is opening new sea lines of communication (SLOCs), significantly shortening maritime trade routes between Asia, Europe, and North America. Control over Greenland would grant the U.S. influence over critical chokepoints, such as the Northwest Passage, enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and sea lane security.
Cost of Maintaining Greenland Trump’s assertion that Denmark struggles to maintain Greenland highlights fiscal and operational challenges. For Denmark, sustaining Greenland’s infrastructure is resource-intensive. U.S. investment in Greenland could bolster economic resilience and enable the development of dual-use infrastructure, supporting both civilian and military objectives.
The Political Dynamics

US-Denmark Relations Trump’s proposal has placed U.S.-Denmark relations under strain. Danish leaders have categorically rejected previous overtures, viewing Greenland as integral to their kingdom’s sovereignty. However, NATO’s collective security commitments and historical cooperation between Washington and Copenhagen suggest room for dialogue. Diplomatic finesse will be key to navigating these sensitivities.
Greenlandic Autonomy Greenland’s self-governing status under the Danish crown complicates negotiations. While some Greenlanders welcome U.S. economic investment, others fear diminished autonomy. Any U.S. initiative would require buy-in from Greenland’s government, balancing their desire for development with respect for their cultural identity and governance.
The Role of International Law The acquisition of Greenland would necessitate adherence to international legal frameworks. Sovereignty under United Nations treaties and Arctic Council agreements protects Greenland’s status. A cooperative approach, rather than unilateral action, would safeguard U.S. legitimacy on the global stage.
International Security Implications
Surveillance and Early Warning Systems Greenland is indispensable to North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) operations. The island’s location facilitates radar coverage essential for detecting intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) launches. Furthermore, Greenland’s geographic advantage strengthens space situational awareness (SSA), ensuring resilience against adversary anti-satellite weapons (ASATs).
Countering Russian Arctic Expansion Russia’s Northern Fleet dominates Arctic naval operations, with a growing arsenal of submarines and icebreakers. By leveraging Greenland’s location, the U.S. can enhance anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities and maritime interdiction operations. This forward presence would act as a counterweight to Russian assertiveness.
A Check on China China’s Arctic ambitions, including investments in Greenlandic mining and scientific research, pose dual-use risks. The U.S. must counter Beijing’s influence to prevent the militarization of Arctic infrastructure. Greenland offers a strategic platform to monitor and disrupt activities that threaten Arctic security.
Potential Outcomes of a US Acquisition

The Best-Case Scenario In an optimal scenario, U.S. acquisition of Greenland enhances NATO’s Arctic strategy, drives sustainable development for Greenland’s population, and strengthens global supply chain security. Investments in renewable energy, critical minerals, and transportation infrastructure could establish Greenland as a center for Arctic innovation.
Worst-Case Scenario Unilateral moves to acquire Greenland risk severe diplomatic fallout, fracturing NATO unity and inviting reprisals from Russia and China. Escalating Arctic tensions could lead to military confrontations, undermining regional stability and global security.
Historical Precedents
The Truman Proposal President Harry Truman’s 1946 offer to purchase Greenland for $100 million highlights historical recognition of the island’s strategic value. Although Denmark rejected the proposal, it set a precedent for U.S. interest in Greenland’s role in Cold War strategy.
Lessons from Alaska and Hawaii The successful integration of Alaska and Hawaii into the United States demonstrates the long-term benefits of strategic acquisitions. These territories have become critical to U.S. economic, military, and geopolitical strength, offering lessons applicable to Greenland.
The Arctic’s Future as a Global Battleground
Climate Change and Emerging Frontiers The Arctic’s rapidly changing environment underscores Greenland’s importance in future conflicts over resources and trade routes. The race to dominate this frontier requires adaptive strategies and robust partnerships.
The Necessity of Multilateral Cooperation While Arctic militarization grows, frameworks like the Arctic Council remain vital for conflict prevention. Collaborative governance, including shared scientific research and environmental stewardship, mitigates the risks of unilateralism.
Conclusion
Greenland’s strategic importance is undeniable. From bolstering national security to securing critical resources, its role in Arctic geopolitics will shape the future of international relations. While President Trump’s vision for U.S. acquisition is ambitious, it highlights the broader stakes in the Arctic’s evolving landscape. Achieving these goals will require a careful balance of diplomacy, economic investment, and military readiness.
FAQs
- Why is Greenland vital for U.S. security? Greenland’s location supports missile defense, Arctic surveillance, and maritime security operations, making it a cornerstone of national security.
- What are rare earth elements, and why are they important? Rare earth elements are critical for military systems, renewable energy technologies, and advanced electronics. Greenland’s reserves reduce reliance on foreign suppliers.
- How does Greenland support Arctic trade routes? Melting ice is opening new shipping lanes like the Northwest Passage. Greenland’s strategic position ensures control over these critical trade routes.
- What are the risks of militarizing the Arctic? Increased militarization heightens tensions with Russia and China, risking conflict and environmental degradation in the Arctic.
- What role does the Arctic Council play? The Arctic Council fosters cooperation on scientific research, environmental protection, and sustainable development, preventing unilateral dominance in the region.